Industrial growth in India has been remarkable over the past few decades. However, this rapid expansion has also brought a pressing challenge—managing wastewater in a sustainable and environmentally responsible way. Traditional wastewater treatment processes often fall short of ensuring complete reuse and recycling, resulting in environmental degradation and water scarcity concerns. This is where zero liquid discharge (ZLD) emerges as a game-changing solution.
By understanding what zero liquid discharge is and how it works, industries across India are now rethinking their wastewater management strategies. Implementing a zero liquid discharge plant or zero liquid discharge system ensures that no liquid waste leaves the facility, thereby minimizing water pollution and promoting water reuse.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Zero Liquid Discharge?
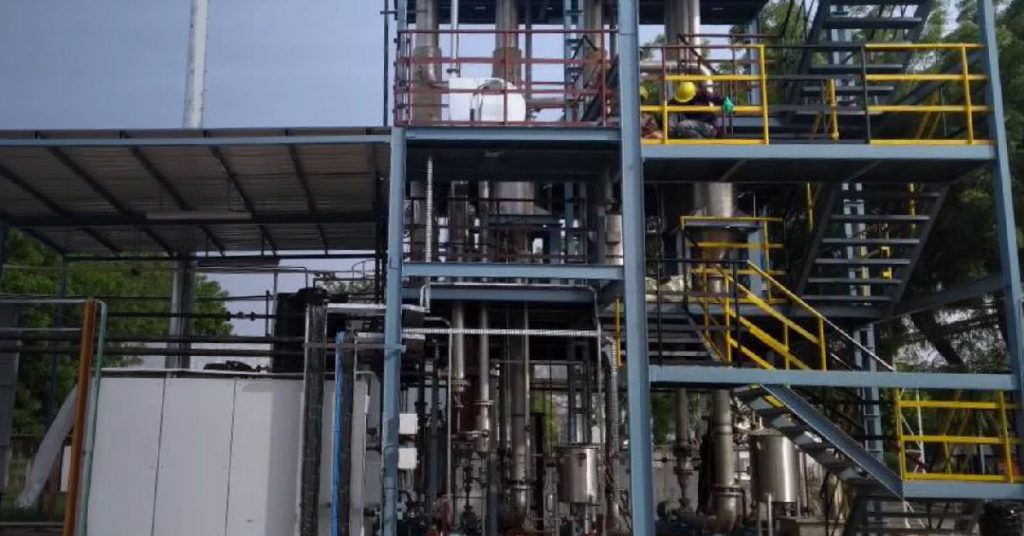
Before diving deeper, it’s important to answer the question: What is zero liquid discharge? Simply put, ZLD is a water treatment process designed to eliminate liquid waste from industrial facilities. This is achieved through advanced filtration, evaporation, and crystallization techniques that recover water for reuse while converting remaining contaminants into solid waste for safe disposal.
Unlike conventional treatment plants that discharge treated water into rivers or sewers, a zero liquid discharge plant ensures that every drop is either recycled back into operations or removed as solid residue. This approach is especially critical in India, where industries often operate in regions facing acute water stress.
The Need for ZLD in India
India is one of the most water-stressed countries in the world. The competition for water between agricultural, domestic, and industrial needs is intensifying. Many industries—such as textiles, power generation, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals—consume large volumes of water and generate equally high volumes of wastewater laden with toxins, heavy metals, and organic pollutants.
Regulatory bodies like the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) have tightened norms, requiring several industries to adopt zero liquid discharge systems. For example, in states like Tamil Nadu and Gujarat, textile and tannery units are mandated to use ZLD to curb pollution in local water bodies. By adopting a zero liquid discharge plant, companies not only meet compliance requirements but also future-proof their operations against water shortages and regulatory risks.
How Zero Liquid Discharge Works?
A zero liquid discharge system typically follows a multi-stage process:
- Pre-Treatment – Removal of large particles, oils, and suspended solids to prepare wastewater for advanced treatment.
- Membrane Filtration – Reverse osmosis (RO) or ultrafiltration to separate clean water from dissolved salts and impurities.
- Evaporation – Thermal processes concentrate the remaining brine.
- Crystallization – Solid salts and other residues are crystallized for safe disposal or potential reuse in certain industries.
- Water Recovery – Up to 95–99% of the water is recovered and reused within the facility.
By closing the loop, a zero liquid discharge plant minimizes the need for freshwater intake and reduces environmental impact significantly.
Advantages of ZLD for Indian Industries
- Regulatory Compliance – With stricter environmental norms, a ZLD system ensures industries meet discharge standards without risk of penalties.
- Water Conservation – By recycling treated water, industries cut down on freshwater dependency, which is critical in drought-prone areas.
- Resource Recovery – Certain ZLD processes allow recovery of by-products such as salts and minerals, which can be sold or reused.
- Sustainability Branding – Adopting a zero liquid discharge plant strengthens an organization’s reputation as an environmentally responsible enterprise.
- Long-Term Cost Savings – While the initial investment can be significant, the reduction in water procurement costs and avoidance of penalties provide long-term financial benefits.
Industry Applications in India
Zero liquid discharge systems are now being implemented across multiple sectors in India:
- Textile and Dyeing Units – High-color, high-salt effluents are treated and reused in production.
- Thermal Power Plants – Cooling tower blowdown is recycled, reducing freshwater intake.
- Pharmaceutical Industry – High-organic-content wastewater is purified to meet strict quality standards.
- Chemical Manufacturing – Hazardous effluents are treated to prevent environmental contamination.
Each industry customizes its zero liquid discharge system to handle its unique effluent composition, flow rates, and recovery targets.
Achieving Sustainable Water Management with Ion Exchange’s ZLD Solutions
Ion Exchange provides advanced and economical solutions to address water scarcity while ensuring environmental sustainability. Our Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems are designed to maximize water recovery, reduce wastewater discharge, and generate substantial cost savings. Backed by over 60 years of expertise, we integrate cutting-edge effluent treatment processes, innovative membrane technologies, and state-of-the-art evaporation methods to help industries achieve complete water reuse. By implementing ZLD, businesses can ensure a consistent water supply for process needs, recover valuable by-products, lower water costs, and significantly reduce their reliance on freshwater sources. Additionally, our solutions enable compliance with pollution control regulations, making them an essential choice for industries striving for sustainability and operational efficiency.
The Future of ZLD in India
As water scarcity intensifies, zero liquid discharge will move from being a compliance requirement to a strategic necessity for industries. The government’s push towards sustainable industrial practices, coupled with growing corporate responsibility, will accelerate the adoption of advanced ZLD technologies.
Innovations such as hybrid ZLD systems, waste heat recovery integration, and automation will make zero liquid discharge plants more energy-efficient and cost-effective. For industries in India, adopting ZLD today is an investment in long-term sustainability and operational security.
Conclusion
Zero liquid discharge is not just a compliance tool—it is a transformative approach to industrial wastewater management in India. By understanding what zero liquid discharge is and implementing an efficient zero liquid discharge system, industries can secure water resources, meet environmental standards, and enhance their brand value.