Water treatment processes are crucial for ensuring the availability of clean and safe water, particularly in a country like India, where water resources are under constant pressure. One of the primary steps in water treatment is screening, a process designed to remove large debris and solid particles. But what is screening in water treatment, and how does it contribute to effective filtration in India? Let’s take a closer look.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Screening in Water Treatment?
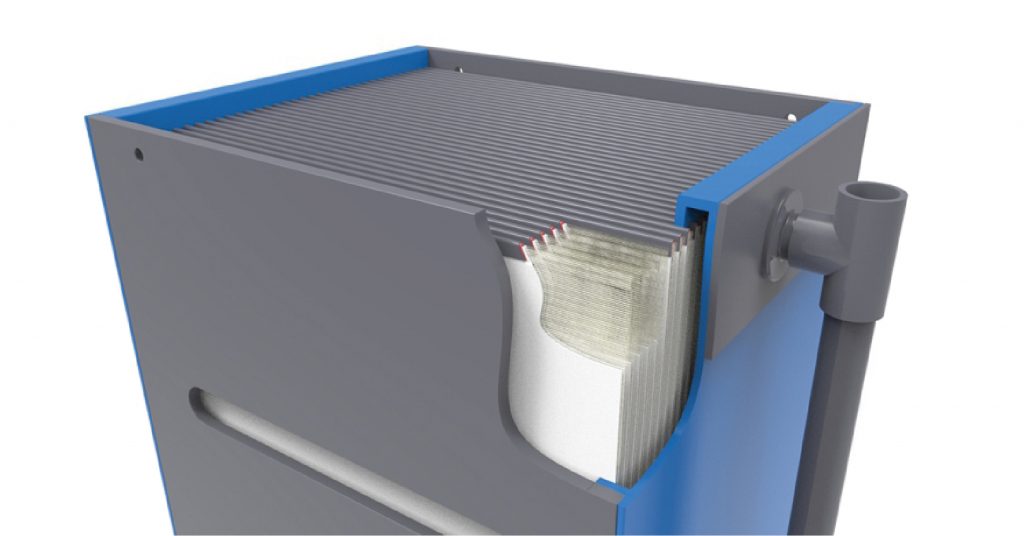
Screening in water treatment is the initial process of separating large debris, such as leaves, plastics, and other solid materials, from water. It involves the use of mechanical screens that allow water to pass through while retaining solid particles. This step is essential to prevent clogging and damage to subsequent filtration and treatment systems.
Types of Screening in Water Treatment
- Coarse Screening:
- Coarse screens are the first line of defense, capturing large objects like sticks, stones, and plastics. They typically have openings ranging from 50 mm to 150 mm.
- Coarse screens are the first line of defense, capturing large objects like sticks, stones, and plastics. They typically have openings ranging from 50 mm to 150 mm.
- Fine Screening:
- Fine screening involves screens with smaller openings, usually ranging from 1 mm to 6 mm. Fine screening in water treatment effectively removes smaller particles, such as sand, silt, and small debris.
- Fine screening involves screens with smaller openings, usually ranging from 1 mm to 6 mm. Fine screening in water treatment effectively removes smaller particles, such as sand, silt, and small debris.
- Micro Screening:
- Micro screens are equipped with extremely fine mesh to capture even smaller particles. These screens are often used as a pre-treatment step in advanced water treatment systems.
The Screening Process in Water Treatment
The screening process in water treatment typically follows these steps:
- Influent Water Collection:
- Raw water is collected and directed to the screening chamber.
- Raw water is collected and directed to the screening chamber.
- Debris Separation:
- Coarse screens remove large debris, preventing damage to downstream equipment.
- Coarse screens remove large debris, preventing damage to downstream equipment.
- Fine Screening:
- Fine screens capture smaller particles that may pass through coarse screens.
- Fine screens capture smaller particles that may pass through coarse screens.
- Screen Cleaning:
- Screens are periodically cleaned to maintain efficiency and prevent clogging.
- Screens are periodically cleaned to maintain efficiency and prevent clogging.
- Disposal of Screened Waste:
- Collected debris is safely disposed of to prevent recontamination.
Why is Screening Essential in Water Treatment in India?
- Preventing Clogging and Equipment Damage:
- Effective screening prevents the accumulation of debris in pipelines and pumps, reducing maintenance costs.
- Effective screening prevents the accumulation of debris in pipelines and pumps, reducing maintenance costs.
- Enhancing Filtration Efficiency:
- By removing larger particles upfront, screening improves the efficiency of downstream filtration processes such as sedimentation and filtration.
- By removing larger particles upfront, screening improves the efficiency of downstream filtration processes such as sedimentation and filtration.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
- In India, water treatment facilities must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines. Effective screening ensures compliance by reducing suspended solids.
- In India, water treatment facilities must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines. Effective screening ensures compliance by reducing suspended solids.
- Optimizing Waste Management:
- The screening process helps in segregating solid waste, making disposal and waste management more efficient.
Applications of Screening in India
- Municipal Water Treatment Plants:
- Screening is widely used in municipal plants to protect pumps and downstream filtration systems from debris.
- Screening is widely used in municipal plants to protect pumps and downstream filtration systems from debris.
- Industrial Water Treatment Systems:
- Industries use screening as a preliminary step to prevent damage to machinery and maintain the efficiency of treatment systems.
- Industries use screening as a preliminary step to prevent damage to machinery and maintain the efficiency of treatment systems.
- Wastewater Treatment Facilities:
- Screening is essential in wastewater treatment to prevent large debris from entering biological treatment processes.
Innovations with Ion Exchange’s INDION Resins
Ion Exchange, under its renowned registered trademark INDION RESINS, offers a comprehensive range of high-performance resins designed for diverse applications. These include a complete suite of cation and anion resins tailored for water and wastewater treatment, as well as uniform particle-size resins optimized for specific requirements. INDION RESINS also caters to specialized needs such as the purification of biodiesel, sugar, food, and beverages.
With advanced formulations, the resins address critical applications like pharmaceutical excipients, catalysts, nuclear-grade requirements, brine softening, heavy metal removal, and adsorbent-grade processes. Additionally, they effectively remove contaminants such as color, odor, organics, nitrate, iron, fluoride, arsenic, and tannin, ensuring unmatched versatility and reliability in purification and treatment solutions.
Conclusion
Screening is a fundamental step in the water treatment process, particularly in regions like India, where water resources must be carefully managed. By effectively removing large and fine debris, screening helps optimize subsequent treatment processes, prevent equipment damage, and ensure the delivery of clean water.