India is facing a critical challenge in managing its water resources. With rising industrial activity, increasing population, and changing climate patterns, the need for efficient water treatment technologies has never been more urgent. One such solution gaining momentum in India is nanofiltration—a versatile and energy-efficient membrane-based process that strikes the right balance between filtration performance and operational cost.
This blog explores the growing applications of the nanofiltration process in water treatment across India, comparing it with reverse osmosis and highlighting where it fits best in the Indian water landscape.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Nanofiltration?
Nanofiltration is a membrane filtration process that lies between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis in terms of filtration capability. Operating at moderate pressures (typically between 4–30 bar), the nanofiltration process is designed to selectively remove divalent and multivalent ions, organic molecules, and certain pathogens while allowing monovalent salts such as sodium and chloride to pass through.
A nanofiltration membrane typically has pore sizes ranging from 1 to 10 nanometers. This makes it particularly useful for applications where partial desalination or targeted removal of contaminants is required without completely stripping essential minerals from the water. This unique characteristic distinguishes nanofiltration from more intensive processes like reverse osmosis.
Nanofiltration vs Reverse Osmosis
One of the most common comparisons in modern water treatment is nanofiltration vs reverse osmosis. While both technologies use pressure-driven membranes to separate impurities from water, they differ in terms of selectivity, energy consumption, and use cases.
Reverse osmosis (RO) is known for its ability to remove nearly all dissolved salts, including monovalent ions. However, this comes with high energy requirements and complete demineralization of water. In contrast, nanofiltration membranes allow certain beneficial minerals to remain in the water while effectively removing harmful substances like hardness-causing ions, pesticides, and organic matter.
For many applications in India, particularly in rural and semi-urban settings, nanofiltration proves to be more cost-effective and suitable, especially where complete deionization is not necessary.
Key Applications of Nanofiltration in India
The nanofiltration process is increasingly being adopted across several sectors in India, owing to its ability to deliver high performance at lower operational costs. Below are some of the key application areas:
1. Groundwater Softening
A significant portion of India relies on groundwater that is rich in calcium and magnesium, leading to hardness issues. Nanofiltration membranes are highly effective in reducing hardness by selectively removing divalent ions while maintaining monovalent ions. This makes NF technology ideal for both domestic and industrial water softening applications.
2. Textile and Dye Wastewater Treatment
India’s textile industry is a major contributor to water pollution, particularly due to the discharge of colored and chemically loaded effluents. Nanofiltration is used in this sector to recover and recycle dye bath water, enabling significant savings on freshwater consumption while meeting discharge norms. The nanofiltration membrane helps retain color and high-molecular-weight compounds, allowing cleaner water to be reused in the process.
3. Drinking Water Purification
In rural and decentralized water systems, nanofiltration is used for removing pesticides, organic contaminants, bacteria, and viruses from surface water and shallow borewells. Since the nanofiltration process does not require extremely high pressure and allows essential minerals to remain, it serves as an efficient and cost-effective alternative to reverse osmosis in community-level drinking water systems.
4. Food and Beverage Industry
Nanofiltration plays a key role in concentration, decolorization, and separation processes in juice production, dairy processing, and beverage formulation. The moderate pressure requirements and selective separation offered by nanofiltration membranes help maintain product quality while optimizing water reuse in these operations.
5. Pharmaceutical Wastewater Treatment
Pharmaceutical manufacturers in India face stringent effluent standards. The nanofiltration process helps in separating complex organic molecules and recovering valuable solvents. It also reduces the load on downstream RO systems by removing high-molecular-weight compounds at an early stage, increasing the overall efficiency of the treatment train.
6. Leather and Tannery Effluents
India’s leather processing hubs in Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh face tough challenges due to high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in tannery wastewater. Nanofiltration is used to recover salts and organics before the RO stage, reducing membrane fouling and improving system performance. This pre-treatment step is critical in achieving Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) compliance.
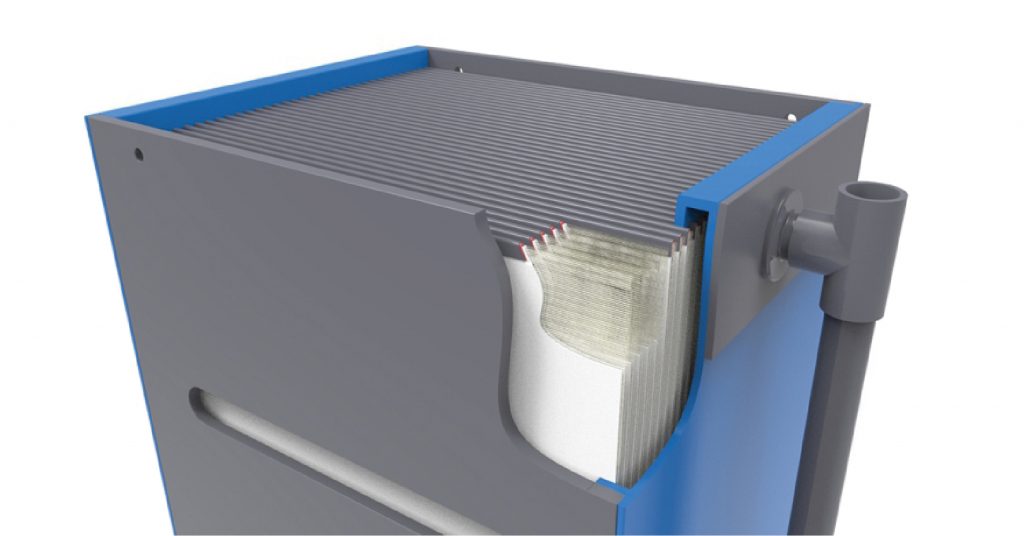
HYDRAMEM Nano Filtration Membranes: Advanced Industrial Solutions by Ion Exchange
HYDRAMEM Cross-Linked Fully Aromatic Polyamide (Thin Film) Composite Nano Filtration Elements (NFEs) are engineered with a durable hard outer shell, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications that require high stability across a range of temperatures and pH levels. These advanced NFEs deliver superior rejection rates for bivalent ion removal, effectively softening brackish water, desalting dyes, treating textile brines, and recovering chemical salts. Their innovative design ensures efficient filtration, contributing to enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings in industrial water treatment processes. Some of our product range includes:
Why Nanofiltration Is Gaining Popularity in India?
There are several reasons why nanofiltration is increasingly preferred across Indian industries and utilities:
- It offers targeted separation, retaining beneficial minerals while removing harmful contaminants.
- Lower pressure requirements make it more energy-efficient than reverse osmosis.
- Nanofiltration membranes have high recovery rates, making the process ideal for water reuse and recycling.
- The technology is scalable and adaptable for small-scale rural water treatment as well as large industrial setups.
- It meets regulatory discharge and quality norms while lowering the cost per litre of treated water.
Conclusion
Nanofiltration is steadily carving its place in India’s water treatment ecosystem. Whether it’s for softening hard groundwater, recycling industrial effluents, or providing safe drinking water in underserved regions, the nanofiltration process offers a compelling combination of performance, affordability, and sustainability. Compared to other technologies, especially in the context of nanofiltration vs reverse osmosis, NF offers a balanced solution that aligns with India’s diverse water treatment needs.
Contact Ion Exchange to explore the best nanofiltration solutions for your industry or community.