India, with its rapidly growing urban population, faces significant challenges in managing and treating wastewater. As cities expand and the demand for sanitation infrastructure increases, efficient and sustainable sewage treatment methods become critical. One of the most widely adopted technologies for treating domestic and industrial wastewater in India is the activated sludge process.
This blog explores how the activated sludge process works, why it is suitable for Indian conditions, and the various types of activated sludge processes used in different treatment setups across the country.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the Activated Sludge Process?
The activated sludge process is a biological wastewater treatment method that uses aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa to break down organic matter in sewage. The process relies on natural microorganisms to consume organic pollutants, converting them into harmless end-products like carbon dioxide, water, and more microbial biomass.
This method is particularly efficient in reducing biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and suspended solids from wastewater, making it an essential step in secondary sewage treatment.
How the Activated Sludge Process Works?
The activated sludge process involves a series of well-coordinated steps:
- Preliminary and Primary Treatment: Before entering the activated sludge tank, sewage undergoes screening and sedimentation to remove large solids, sand, and grit. This ensures smoother operation and prevents clogging in downstream units.
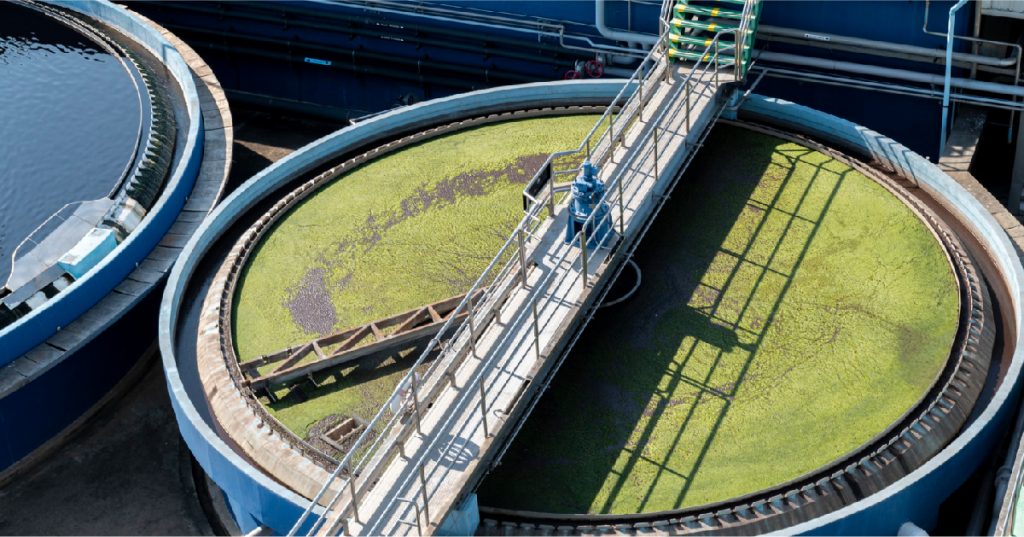
- Aeration Tank: In this stage, the wastewater is mixed with a portion of recycled sludge known as “activated sludge” and is continuously aerated using diffusers or mechanical aerators. The oxygen supports the growth of aerobic microorganisms that consume organic pollutants.
- Biological Reaction: Microorganisms feed on the organic matter in the sewage, forming clumps or “flocs.” These flocs are responsible for breaking down the waste material into simpler compounds. The process typically lasts for 4 to 8 hours, depending on the system design and waste load.
- Secondary Clarifier (Settling Tank): After aeration, the mixture flows into a settling tank where the sludge (composed of microbial biomass) settles at the bottom, and the treated effluent overflows from the top. A portion of this settled sludge is returned to the aeration tank to maintain microbial concentration, while excess sludge is removed for further treatment or disposal.
- Effluent Discharge or Tertiary Treatment: The treated water can be safely discharged into rivers or reused for gardening, industrial processes, or groundwater recharge. In some cases, additional treatment (like filtration or disinfection) is done to meet stricter discharge standards.
Types of Activated Sludge Process
India’s diverse geography, climate, and urban layout require flexible wastewater treatment solutions. As a result, different types of activated sludge processes are used based on the volume of wastewater, space availability, and local requirements. Here are some commonly implemented types in India:
- Conventional Activated Sludge Process: This is the standard method where wastewater is aerated in large tanks, and microorganisms are allowed to consume organic material. It is widely used in medium to large municipalities.
- Extended Aeration: This variation operates with a longer aeration time and lower organic loading. It is particularly suitable for small towns, residential colonies, and decentralized sewage systems due to its low sludge generation and ease of maintenance.
- Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR): In SBR systems, all steps—fill, aerate, settle, decant, and idle—occur in the same tank but at different times. These are gaining popularity in Indian cities and smart townships for their space efficiency and automated operation.
- Oxidation Ditch: This is a modified extended aeration process where wastewater circulates in a loop-shaped ditch with continuous aeration. It’s ideal for semi-urban and rural settings, offering good performance with minimal supervision.
- Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): A combination of the activated sludge process and membrane filtration, MBR provides superior effluent quality. Though costlier, it is increasingly used in high-value applications like hospitals, IT parks, and high-rise residential complexes.
Advantages of the Activated Sludge Process in India
- High Efficiency: It effectively reduces organic load, BOD, and pathogens.
- Adaptability: Various types allow customization to suit different scales and needs.
- Reuse Potential: Treated water can be reused for non-potable purposes, promoting water conservation.
- Compliance: Helps meet pollution control norms set by CPCB and local authorities.
Challenges and Considerations
While the activated sludge process is highly effective, it comes with certain challenges:
- Energy Intensive: Continuous aeration demands significant electricity.
- Sludge Handling: Excess sludge requires careful disposal or further treatment.
- Operation and Maintenance: Skilled staff and regular monitoring are essential for consistent performance.
Activated Sludge Process by Ion Exchange: Efficient Biological Wastewater Treatment
The Activated Sludge Process is a widely used biological wastewater treatment method that utilizes an aeration tank containing suspended microorganisms, known as Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS), to break down the organic matter present in the effluent. The treated water then moves to a secondary clarifier, where the MLSS settles, and the sludge is partially recirculated back into the aeration tank to maintain microbial activity. Oxygen or air is supplied through either surface or diffused aeration systems to sustain the microorganisms. The process operates with a Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) of approximately 6–7 hours and a Sludge Retention Time (SRT) ranging from 8–15 days, ensuring effective organic matter degradation and wastewater purification. With Ion Exchange’s advanced treatment solutions, industries can achieve superior wastewater management, enhanced efficiency, and environmental compliance.
Conclusion
The activated sludge process plays a vital role in treating sewage across India, helping cities and towns manage wastewater in an environmentally responsible way. By adopting the right types of activated sludge processes, municipalities and industries can ensure cleaner water bodies, healthier ecosystems, and better public health outcomes.